In the ever-evolving landscape of finance, the marriage between private markets and insurance has garnered significant attention. This union, marked by the acquisition of insurers by private equity giants, brings forth both promises of growth and concerns about potential risks. Let’s delve into this complex dynamic to understand its implications for the industry and beyond.
Private equity firms like Blackstone, Apollo, and KKR have been expanding their presence in the insurance sector, acquiring insurers and reshaping their business models. This trend gained momentum post-2008 financial crisis, as private markets emerged as the new kings of Wall Street, wielding substantial influence and capital. The allure of the insurance industry lies in its vast market potential and stable revenue streams, particularly in products like fixed annuities.
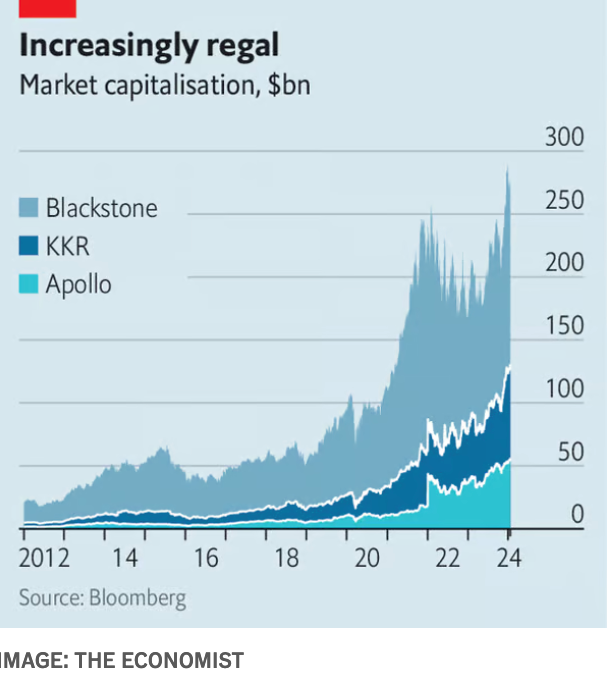
The expansion of private markets into insurance brings several potential benefits. For insurers, partnering with private equity firms offers access to significant capital and expertise in asset management. Private equity firms, on the other hand, see insurers as a means to deploy their capital in stable, long-term investments. This symbiotic relationship can lead to enhanced diversification of insurers’ portfolios and improved returns for investors.
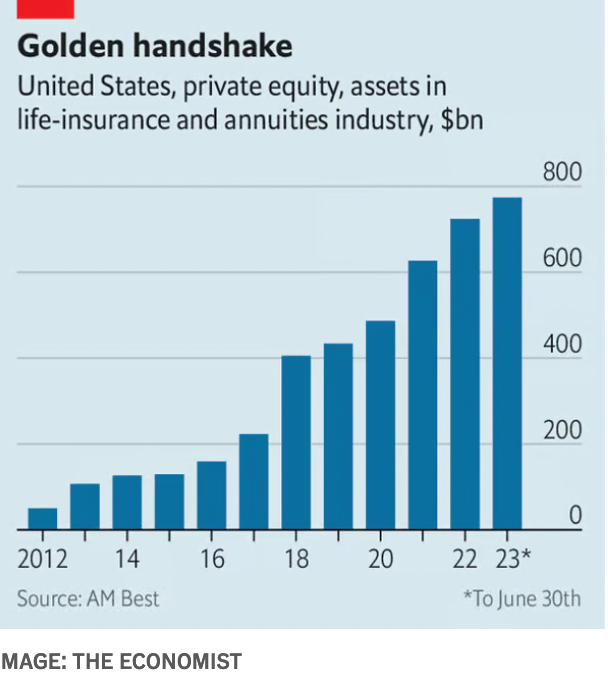
However, this convergence of private markets and insurance also raises significant concerns. One key issue is the potential risk to policyholders and financial stability. The influx of private capital into the insurance industry may lead to increased exposure to risky assets and complex financial instruments. Moreover, the regulatory framework governing insurers may not be equipped to effectively monitor and mitigate these risks.
Another concern is the rise of offshore reinsurance transactions, which involve insurers transferring risk to entities based in jurisdictions with lax regulatory oversight. While these deals may offer short-term financial benefits, they can also increase opacity and undermine the capital strength of the industry.
The recent example of Eurovita, a conglomerate of Italian life insurers acquired by a private equity firm, serves as a cautionary tale. Poor asset-liability management and weak policyholder protections led to a capital shortfall and eventual regulatory intervention. This episode underscores the importance of robust risk management and regulatory oversight in the insurance industry.
Moving forward, regulators and industry stakeholders must collaborate to address the challenges posed by the intersection of private markets and insurance. Enhanced transparency, stronger capital requirements, and stricter oversight of offshore transactions are essential steps to safeguard policyholders and ensure the stability of the financial system.
Despite the risks, the convergence of private markets and insurance also presents opportunities for innovation and growth. By leveraging private capital and expertise, insurers can develop new products and expand their market reach. Similarly, private equity firms can diversify their investment portfolios and generate attractive returns for their investors.
The integration of private markets and insurance represents a complex and multifaceted phenomenon with both risks and opportunities. While it holds the potential to drive growth and innovation, it also requires careful consideration of the associated risks and regulatory challenges. By navigating these challenges effectively, insurers and private equity firms can forge mutually beneficial partnerships that contribute to the resilience and prosperity of the insurance industry.
